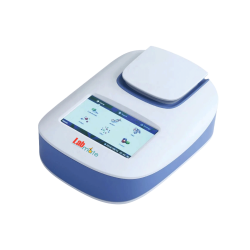
Fluorometer LMFMR-A102 is a benchtop dual-channel fluorometry meticulously crafted to ensure the accurate detection of highly sensitive fluorescence signals while allowing the quantification of DNA, RNA, and proteins. With precision excitation filters at 460 ± 20 nm and 525 ± 20 nm, it boasts an impressive sensitivity, detecting DNA at levels as low as 0.5 ng/ul. Provides dual-channel fluorescence capabilities, featuring both blue and green channels for measuring the concentration of the sample.
Get Quote| Dynamic Range | Five orders of magnitude |
| Linear Dynamic Range | R² >0.995 |
| Processing Time | 3s (Once) |
| Light Source | Blue LED, Green LED |
| Excitation Filters | 460 ± 20 nm, 525 ± 20 nm |
| Emission Filters | 525 to 570 nm (45 nm), 575 to 640 nm (65 nm) |
| Detector | Photodiode |
| Repeatability | <1.5 % |
| Stability | <1.5 % |
| Sensitivity | ds DNA: 0.5 ng/ml |
| Dimension | 194 × 155 × 72.5 mm |
| Weight | 0.4 kg |
 Crafted with a user-friendly 4.3-inch touchscreen ensures effortless operation
Crafted with a user-friendly 4.3-inch touchscreen ensures effortless operation
 Quik reading in just 3 seconds for DNA, RNA, and protein analysis
Quik reading in just 3 seconds for DNA, RNA, and protein analysis
 Wide linear dynamic range spanning five orders of magnitude for versatile analytical capabilities
Wide linear dynamic range spanning five orders of magnitude for versatile analytical capabilities
 Equipped with dual fluorescence channels, it excels at comprehensive quantification of both nucleic acids and proteins in a single measurement
Equipped with dual fluorescence channels, it excels at comprehensive quantification of both nucleic acids and proteins in a single measurement
 Offers convenience with an adaptable open system, compatible with PCR tube adapters
Offers convenience with an adaptable open system, compatible with PCR tube adapters
 Ensures secure data management by accommodating up to 1,000 datasets, with easy data export through a USB port
Ensures secure data management by accommodating up to 1,000 datasets, with easy data export through a USB port
 Employs high-intensity light-emitting diode (LED) as a light source, to provide excitation light at a specific wavelength
Employs high-intensity light-emitting diode (LED) as a light source, to provide excitation light at a specific wavelength
Adapter for 0.5ml qPCR tube
Adapter for 0.2ml qPCR tube
It finds application in handling rare and challenging samples, especially those with limited quantities of DNA, RNA, or proteins post-extraction. It is also indispensable in costly experiments like qPCR, PCR cloning, transfection, and next-generation sequencing.
Get Quote for
Fluorometer LMFMR-A102
Related Products